Customers seeking the core principles of marketing want a simple answer rather than a deep dive into complicated marketing theories. With marketing surrounding us, whether it be online ads, social media, emails, stores, or apps, it uses the core concepts of marketing as the basic building blocks. These concepts offer insight into customer buying behavior, business value creation, and the sustainability of growth.
This article aims to simplify the information available, utilizing charts, scenarios, and infographics to maximize the reader’s comprehension.
What Are the Core Concepts of Marketing?
Core Concepts of Marketing. Marketing’s core concepts are the fundamental building blocks of every marketing function. These concepts aid the understanding of customer behavior, product design, value communication, and the formation of enduring partnerships. Put simply, Marketing is not about selling a product. It’s about understanding the customer.
Core Concepts of Marketing Management
Marketing management uses these concepts to plan, execute, and control marketing activities.
| Area | Role in Marketing Management |
| Customer needs | Decide what to offer |
| Value creation | Shape product and pricing |
| Exchange | Enable buying & selling |
| Relationships | Build loyalty |
| Market selection | Focus on right audience |
These concepts guide strategy, budgeting, promotion, and growth decisions.
5 Core Concepts of Marketing
This section targets:
5 core concepts of marketing, explain core concepts of marketing
1. Needs, Wants, and Demands
This is the starting point of all marketing.
| Term | Simple Meaning | Example |
| Needs | Basic human requirement | Food, shelter |
| Wants | Desired form of need | Burger instead of food |
| Demands | Wants + ability to pay | Ordering burger online |
Marketing identifies demands, not just wants.
2. Product and Services
A product or service is anything that satisfies a need.
| Type | Meaning | Example |
| Product | Physical item | Smartphone |
| Service | Intangible offer | Internet connection |
| Benefit | Problem solved | Communication |
Customers don’t buy products — they buy benefits.
3. Value and Customer Satisfaction
This decides success or failure.
| Concept | Meaning | Result |
| Value | Benefits vs price | Purchase decision |
| Satisfaction | Post-use happiness | Repeat buying |
| Experience | Total journey | Brand loyalty |
High value + satisfaction = long-term customers.
4. Exchange and Relationships
Marketing is based on exchange of value.
| Element | Meaning | Example |
| Exchange | Value for value | Money for product |
| Relationship | Long-term connection | Subscriptions |
| Trust | Confidence in brand | Repeat customers |
Modern marketing focuses on relationships, not one-time sales.
5. Market and Target Customers
You cannot serve everyone.
| Market Factor | Explanation |
| Market | Group of potential buyers |
| Target market | Selected customer group |
| Segmentation | Dividing customers |
| Positioning | Brand image in mind |
Good marketing chooses who NOT to target.
Core Concepts of Marketing – One Summary Table
| Concept | What It Explains | Why It Matters |
| Needs & wants | Why people buy | Product planning |
| Product & service | What is offered | Customer choice |
| Value | Why brand is chosen | Competitive edge |
| Exchange | How buying happens | Revenue |
| Market | Who to serve | Focused growth |
Core Concepts of Marketing With Examples
| Brand | Core Concept Used | How |
| Apple | Value & experience | Premium design |
| Amazon | Customer satisfaction | Fast delivery |
| Netflix | Market segmentation | Personalized content |
| Nike | Emotional value | Motivation & identity |
| Starbucks | Relationship marketing | Loyalty programs |
Marketing Mix – Practical Application of Concepts
The 4Ps of Marketing
| P | Meaning |
| Product | What you sell |
| Price | What customer pays |
| Place | Where it’s available |
| Promotion | How you communicate |
Extended 7Ps (For Services)
| Extra Ps | Why Needed |
| People | Service quality |
| Process | Smooth delivery |
| Physical evidence | Trust & experience |
Importance of Marketing Concepts
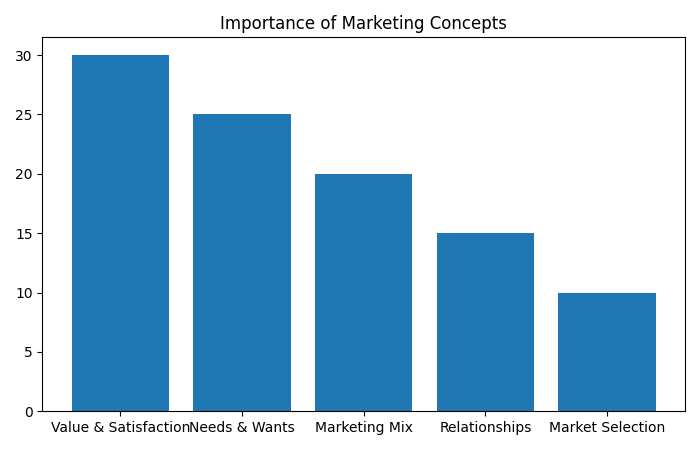
| Concept | Usage % |
| Value & Satisfaction | 30 |
| Needs & Wants | 25 |
| Marketing Mix | 20 |
| Relationships | 15 |
| Market Selection | 10 |
Shows customer value is the top priority.
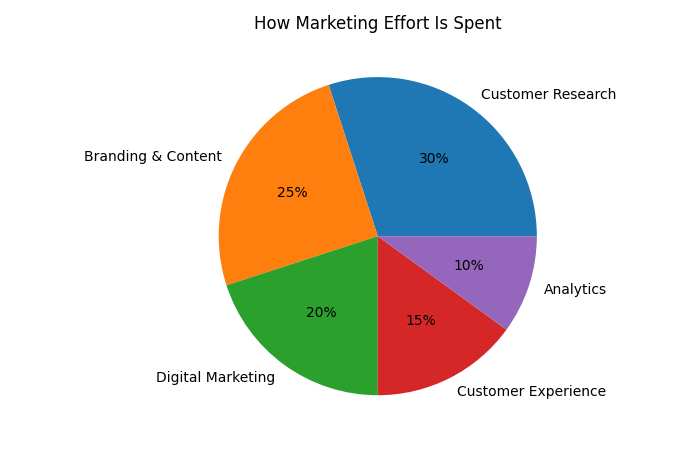
How Marketing Effort Is Spent
| Activity | Share |
| Customer Research | 30% |
| Branding & Content | 25% |
| Digital Marketing | 20% |
| Customer Experience | 15% |
| Analytics | 10% |
Businesses invest more in trust and information today.
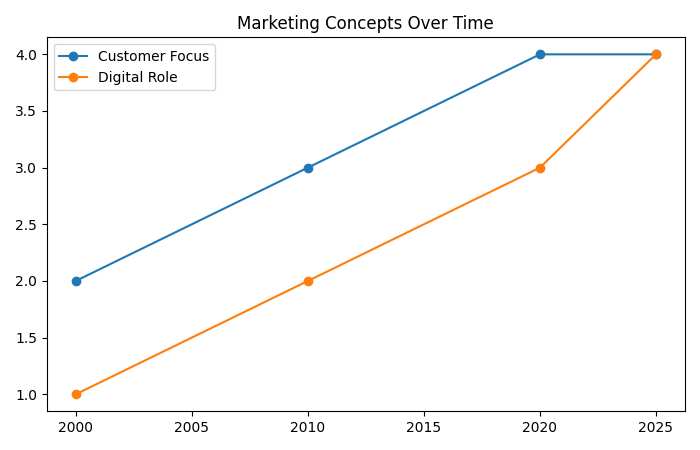
Marketing Concepts Over Time
| Year | Customer Focus | Digital Role |
| 2000 | Medium | Low |
| 2010 | High | Medium |
| 2020 | Very High | High |
| 2025 | Very High | Very High |
Tools change, concepts remain.
Core Concepts of Marketing vs Selling
| Marketing | Selling |
| Builds interest | Closes deal |
| Long-term | Short-term |
| Customer-focused | Product-focused |
| Value creation | Revenue generation |
Marketing prepares customers. Selling completes the process.
Why Core Concepts of Marketing Still Matter Today
Even with AI, automation, and digital ads:
- People still have needs
- Value still drives decisions
- Trust still beats price
Technology changes. Human behavior doesn’t.
Core Concepts vs Marketing Management
| Marketing Concepts | Marketing Management |
| Ideas & theory | Practical execution |
| Customer-focused | Business-focused |
| Long-term view | Short + long term |
| Value creation | Profit planning |
Marketing management applies these concepts in real life.
How These Concepts Work Together
| Step | Concept |
| Understand people | Needs & wants |
| Create offer | Product & service |
| Set value | Price & satisfaction |
| Deliver | Exchange |
| Retain | Relationships |
This is marketing in action.
Final Conclusion
The core concepts of marketing explain how businesses and customers connect. Marketing is not about tricks or pressure. It is about understanding people, creating value, and building trust.
If someone understands these concepts clearly, they can:
- Plan better strategies
- Create meaningful products
- Build loyal customers
- Grow sustainably
In short:
Marketing starts with people and ends with relationships.